Hot-dip galvanizing treatment (according to UNE EN ISO 1461 standard)
At Insametal, we are specialists in the design, manufacture and assembly of metal protections for bridges and viaducts in railway and road works. We know that our metal structures are constantly exposed to extreme environmental conditions, which makes it essential to ensure their durability and resistance. This is where the hot dip galvanized plays a crucial role.
That is why we are proud to offer this service, which is essential for protecting metal structures from corrosion. The treatment, which strictly follows the UNE EN ISO 1461 standard, guarantees a long service life and excellent performance of the treated materials, even in the most adverse conditions.
What is the hot dip galvanized?

Hot-dip galvanizing is a process whereby a layer of zinc is applied to the surface of steel or iron by immersing the material in a bath of molten zinc at approximately 450°C. This coating not only acts as a physical barrier against corrosive agents, but also offers electrochemical protection, ensuring that even if the layer is damaged, the zinc will continue to protect the base metal through a sacrificial corrosion process.
Aspects such as coating thickness, uniformity or adherence are established thanks to the UNE EN ISO 1461 standard, ensuring that the treated products meet the quality and durability standards required for their industrial and structural applications.
Procedure
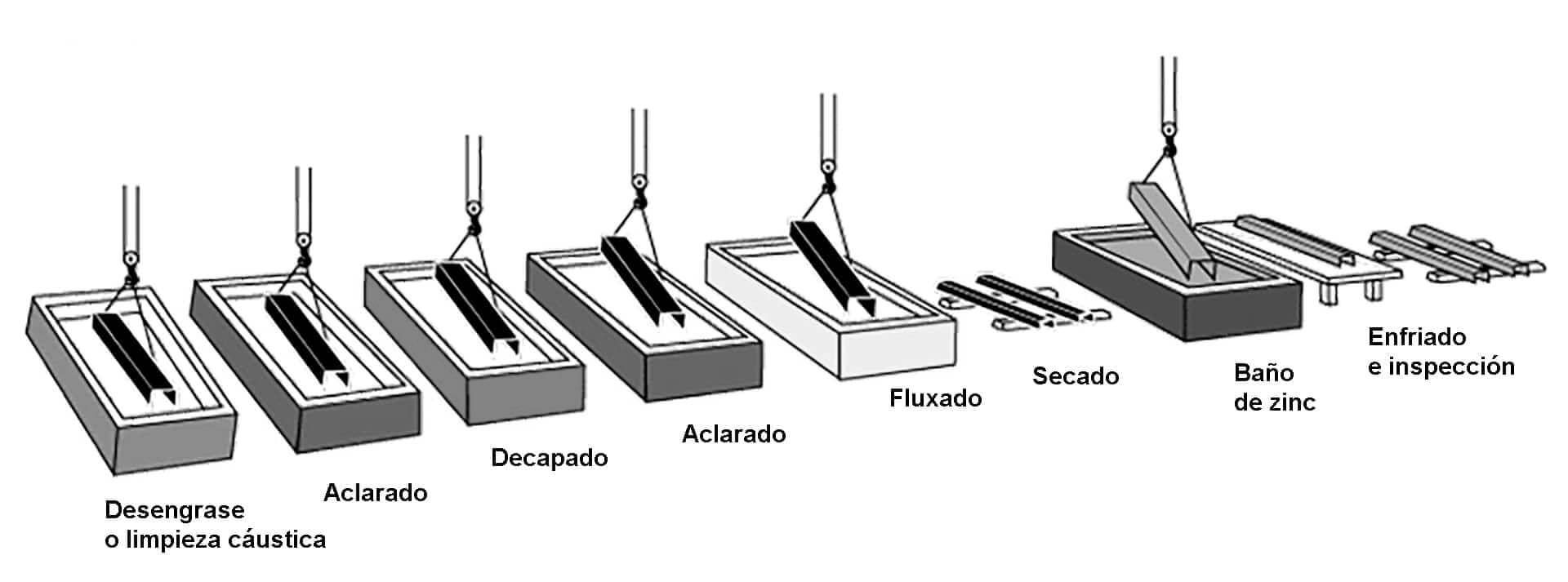
- Preparation of Material:
-
- Inspection: A visual inspection of the material is carried out to ensure that it is in suitable condition for galvanizing.
- Cleaning: Steel goes through a cleaning process that includes degreasing, pickling and rinsing to remove oxides, oils and other contaminants.
- Rinse
2. Pickling:
-
- The steel is dipped in a hydrochloric acid solution to remove oxides and any traces of rust. This process ensures that the steel surface is free of impurities.
- The piece is then clarified.
3. Fluxed:
-
- After pickling, the steel is dipped in a solution of zinc chloride and ammonium chloride, known as flux, to prevent surface oxidation prior to immersion in the zinc and to improve the adhesion of the zinc during immersion.
- Once the procedure has been carried out, the piece is allowed to dry.
4. Galvanized:
-
- The steel is dipped into a bath of molten zinc at approximately 450 degrees Celsius. The duration of immersion and the temperature of the zinc are carefully controlled to ensure uniform zinc coverage.
5. Cooling and Solidification:
-
- After immersion, the galvanized steel is removed from the bath and rapidly cooled by water or air to solidify the zinc layer. This process may include slow or rapid cooling, depending on the requirements of the final product.
6. Final Inspection:
-
- A visual inspection and additional tests, such as measuring the thickness of the zinc layer, are carried out to ensure that it meets established quality standards.
7. Finish:
-
- Depending on the final application, galvanized material may undergo additional processes, such as slag or burr removal, to ensure a proper finish.
Advantages of hot dip galvanizing
Hot-dip galvanizing offers numerous advantages over other corrosion protection methods, such as:
- Long service life: Zinc coatings applied according to UNE EN ISO 1461 can provide a service life of several decades, even in aggressive environments such as coastal or industrial areas.
- Low maintenance: Once galvanized, steel does not require excessive periodic maintenance, which significantly reduces long-term costs.
- Comprehensive protection: Unlike other coating methods, hot-dip galvanizing protects both exterior and interior surfaces, including hard-to-reach areas such as cavities and angles.
- Sustainability: Zinc is a recyclable material, and the galvanizing process generates less waste compared to other protection methods.
Regulations
The regulations to be followed depend on the geographical area. In Spain, the Spanish regulations that come from the European and International regulations (EN … / ISO …) must be complied with:
-
- UNE-EN ISO 1461:2023 : Hot-dip galvanising coatings on iron and steel parts - Specifications and test methods. (ISO 1461:2022)
-
- UNE-EN 1090-2:2019: Execution of steel and aluminium structures - Part 2: Technical requirements for steel structures.
INSAMETAL S.A.
Insametal's commitment to quality
At Insametal, we are committed to offering hot-dip galvanising solutions that meet and exceed our customers' expectations. We strictly comply with the UNE EN ISO 1461 standard, ensuring that each project is carried out to the highest standards of quality and efficiency. Thus, these structures remain functional and safe for many years, withstanding the demands of rail and road traffic.
We ensure that each project exceeds our clients' most rigorous expectations, offering solutions that not only stand the test of time, but also guarantee the safety and efficiency of infrastructures.
So, trust Insametal to protect what really matters. Our commitment to quality and durability is reflected in every structure we design. Don't put your projects at risk; choose the protection that only perfect hot-dip galvanizing by Insametal can offer. Contact us and ensure the success of your next project!
We use this type of procedure to provide a protective layer to our products, giving them a significant improvement in their durability and appearance. Some of the products that usually have this type of coating are: road railings.
You can find more information about our products at www.insametal.es


















